What is Self-Funding
Self-funding is an alternative financial strategy to costly traditional benefits insurance. With a self-funding strategy, the employer, not an insurance company, assumes direct responsibility for providing health care benefits to his/her employees, while also managing the assets of the plan. While a company can choose to administer their plan completely by themselves, most typically work with a third party administrator (TPA). The TPA helps to set up a benefits plan design that best meets the unique needs of a company’s workforce, as well as pay eligible claims and maintain, track and generate health records and reports.
Why do companies choose to self-fund their benefits?
Perhaps the greatest self-funding advantage is improved cash flow for the employer. Employers set aside funds in an interest-bearing account until they’re needed to pay a claim. Because a self-funded strategy enables employers to pay for each claim as it’s incurred rather than paying a fixed premium to a traditional carrier, the employer has full use of working capital and interest earnings of any monies in the fund throughout the year. The TPA works with the company to help it determine how much to set aside to cover predictable and unpredictable claims. By self-funding predictable claims, the end result is a direct savings of medical insurance premium. Employers purchase stop-loss insurance to cover any unpredictable claims, such as catastrophic illnesses or injuries.
What are main advantages of self-funding
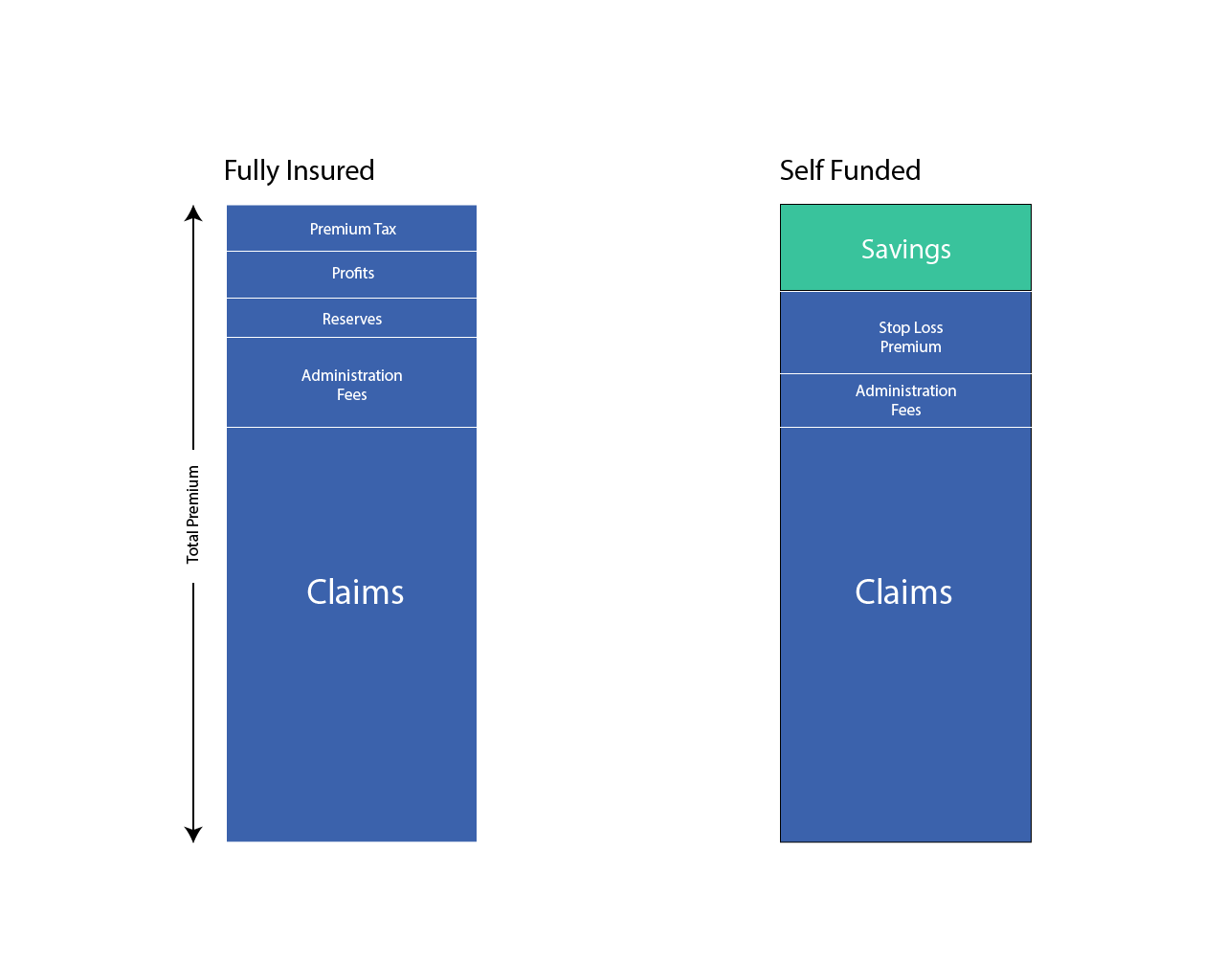
A properly designed and administered self-funded plan can realize as much as 30 percent savings over a traditional-style plan, while mirroring or enhancing the traditional plan’s benefit design.
Other self-funding advantages include:
- Greater employer control.As opposed to purchasing a one-size-fits-all plan from an insurer, the employer and its TPA are able to develop a benefits plan custom tailored to that employer’s workforce. This enables the employer to develop programs that address the specific health issues affecting his or her workforce, not just the broader population covered by a traditional insurer.
- Reduction in risk, retention and overhead.Because only a portion of total self funded plan costs are composed of insurance premiums, these amounts are reduced.
- Good experience.. Stop-loss insurance protects employers in “bad claims” years. Savings in paid claims are immediately available in “good claims” years. And because the employer maintains control over health plan reserves, interest income is maximized. This is income that would be otherwise generated by an insurance carrier through investment of premium dollars.
- Easier review of progressive claims.TPAs regularly review a company’s claims information to determine if there are specific needs areas to address. Online technology tools can be provided to help employers look at their claims database many different ways to determine how best to spend their wellness and prevention budget.
- Not subject to state regulations and mandates.The employer is not subject to conflicting state health insurance regulations and mandates. Self-funded plans are federally regulated under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA).
- Not subject to state insurance premium taxes.This accounts for approximately two to three percent of a premium dollar’s value.
Fully-Insured vs. Self-Funded Plan Cost Comparison